
When I choose between lithium and alkaline batteries, I focus on how each type performs in real-world devices. I often see alkaline battery options in remote controls, toys, flashlights, and alarm clocks because they offer reliable power and cost savings for everyday use. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, work best in high-drain gadgets like smartphones and cameras due to their higher energy density and rechargeability.
| Battery Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| Alkaline Battery | Remote controls, toys, flashlights, alarm clocks, radios |
| Lithium Battery | Smartphones, tablets, cameras, high-drain electronics |
I always consider what matters most for my device—power, value, or environmental impact—before making a choice. The right battery depends on the device’s demands and my priorities.
The best battery choice balances performance, cost, and environmental responsibility.
Key Takeaways
- Lithium batteries deliver steady, strong power and last longer in high-drain devices like cameras and smartphones.
- Alkaline batteries offer reliable, affordable power for low-drain devices such as remote controls and clocks.
- Lithium batteries perform well in extreme temperatures and have a longer shelf life, making them ideal for outdoor and emergency use.
- Although lithium batteries cost more upfront, they save money over time through longer life and rechargeability.
- Proper recycling and storage of both battery types protect the environment and extend battery reliability.
Performance Comparison
When I compare lithium and alkaline batteries in real-world devices, I notice a clear difference in power output, especially under heavy use. Lithium batteries deliver a steady 1.5V throughout their discharge cycle. This means my high-drain devices, like game controllers and smart locks, keep working at peak performance until the battery is nearly empty. In contrast, an alkaline battery starts at 1.5V but loses voltage steadily as I use it. This drop can cause electronics to slow down or stop working sooner than I expect.
Laboratory tests confirm what I see in daily use. Here’s a table that shows how lithium and alkaline batteries perform under continuous load:
| Parameter | Lithium (Voniko) AA Battery | Alkaline AA Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 1.5 V (stable under load) | 1.5 V (drops significantly under load) |
| Capacity at 0.2C Rate | ~2100 mAh | ~2800 mAh (at low discharge rates) |
| Capacity at 1C Rate | ≥1800 mAh | Significantly reduced due to voltage drop |
| Internal Resistance | <100 mΩ | Higher internal resistance causing voltage drop |
| Peak Current Capability | ≥3 A | Lower, poor performance at high drain |
| Voltage Drop at 1A Load | ~150-160 mV | Higher voltage drop, reduced power output |
| Flash Recycle Performance | 500+ flashes (professional speedlight test) | 50-180 flashes (typical alkaline) |
Lithium batteries maintain higher and more stable voltage and power output, especially in demanding devices like LED panels and cameras. Alkaline batteries lose effectiveness quickly under similar conditions.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries provide stronger and more reliable power for high-drain devices, while alkaline batteries may struggle to keep up under continuous heavy use.
Consistency Over Time
I always look for batteries that deliver steady performance from start to finish. Lithium batteries stand out because they keep their voltage stable throughout most of their usable life. My digital cameras and high-performance electronics run smoothly without sudden drops in power. On the other hand, an alkaline battery gradually loses voltage as it discharges. This decline can lead to weaker flashlight beams or slower response in toys and remotes as the battery nears the end of its life.
The higher energy density and longer lifespan of lithium batteries also mean I replace them less often. I find this especially helpful in devices that need a constant, reliable power supply.
Devices that require steady voltage, such as cameras and advanced electronics, benefit most from lithium batteries’ consistent output.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries deliver stable voltage and consistent performance over time, making them ideal for electronics that need reliable power throughout the battery’s life.
Lifespan and Shelf Life
Battery Life in Use
When I compare battery life in real-world use, I see a clear difference between lithium and alkaline options. Lithium batteries, especially lithium-ion types, deliver much longer operational lifespans in high-drain devices. For example, my rechargeable lithium-ion batteries can last from 500 to 2,000 charge cycles. In my experience, this means I can use them in my smartphone or camera for years before needing a replacement. In contrast, a typical AA alkaline battery powers a high-drain device for about 24 hours of continuous use. I notice this difference most when I use flashlights. Lithium batteries keep my flashlight running longer, especially at higher brightness levels, while alkaline batteries deplete faster under the same conditions.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Battery Type | Average Usable Lifespan | Shelf Life | Performance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 500 to 2,000 charge cycles | 2 to 3 years | Great for high-drain devices; lasts >1 day in smartphones with heavy use |
| AA Alkaline | ~24 hours continuous use in high-drain devices | 5 to 10 years | Better in low-drain devices; depletes faster under heavy load |
Lithium batteries provide longer operational life in demanding devices, making them ideal for electronics that require frequent or extended use.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries last much longer in high-drain devices and support more charge cycles than alkaline batteries.
Shelf Life When Stored
When I store batteries for emergencies or future use, shelf life becomes important. Both lithium and alkaline batteries can last up to 10 years at room temperature with only moderate capacity loss. I always store my alkaline batteries in a cool, dry place with about 50% humidity. Freezing is not recommended, as it can damage the battery. Lithium batteries have very low self-discharge rates, especially when I store them partially charged at around 40%. This helps maximize their shelf life. I find lithium batteries easier to rely on for long-term storage because they do not leak and maintain their capacity better over time.
- Both battery types can be stored at room temperature for up to 10 years.
- Alkaline batteries are simple to store and require only basic precautions.
- Lithium batteries need to be stored partially charged to prevent damage.
- Lithium batteries maintain capacity better and do not leak, even after many years.
Proper storage ensures both battery types remain reliable for years, but lithium batteries offer superior long-term stability.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries maintain their charge and integrity longer in storage, making them a dependable choice for long-term backup.
Cost and Value
Upfront Price
When I shop for batteries, I notice that lithium batteries usually cost more than their alkaline counterparts. For example, a two-pack of Energizer AA lithium batteries often retails for about $3.95, while a four-pack can reach $7.75. Larger packs, such as eight or twelve, offer a better price per battery but still remain higher than most alkaline options. Some specialty lithium batteries, like AriCell AA Lithium Thionyl, can cost as much as $2.45 for a single unit. In comparison, standard alkaline batteries typically sell for less per unit, making them attractive for buyers focused on immediate savings.
| Quantity (pcs) | Brand/Type | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | AA Lithium | $3.95 |
| 4 | AA Lithium | $7.75 |
| 8 | AA Lithium | $13.65 |
| 12 | AA Lithium | $16.99 |
| 1 | AA Lithium | $2.45 |
Lithium batteries require a higher upfront investment, but their performance often justifies the cost for demanding applications.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries cost more initially, but their superior performance can make them worthwhile for specific needs.
Long-Term Value
I always consider the total cost of ownership when choosing batteries for devices I use every day. Although alkaline batteries have a lower purchase price, I find that they drain quickly in high-drain devices, leading to frequent replacements. This pattern increases my overall spending and creates more waste. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries, while more expensive at first, can be recharged hundreds or even thousands of times. This reusability means I buy fewer batteries over time, which saves money and reduces environmental impact.
- Alkaline batteries have a high cost per kilowatt-hour, especially in devices that run daily.
- Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries offer a lower cost per kilowatt-hour when I factor in their long lifespan and reduced replacement frequency.
- A single rechargeable lithium-ion AA battery can replace up to a thousand single-use batteries, providing significant savings.
- Using lithium-ion batteries also means fewer last-minute trips to the store and less battery waste in landfills.
Over time, lithium-ion batteries deliver better value and sustainability, especially for high-drain or frequently used electronics.
Summary Point:
Lithium-ion batteries offer greater long-term savings and convenience, making them a smart choice for daily-use and high-drain devices.
Device Compatibility
Best for High-Drain Devices
When I select batteries for high-drain devices, I always look for options that deliver steady power and long life. Devices like digital cameras, portable gaming consoles, and GPS units demand a lot of energy in a short time. In my experience, lithium batteries outperform others in these situations. Manufacturers design most DSLR and mirrorless cameras to use lithium-ion rechargeable batteries because they provide high power capacity in a compact size. I notice that lithium batteries also work well in extreme temperatures, which makes them reliable for outdoor photography or travel.
Photographers and gamers often choose lithium batteries for their consistent voltage and ability to handle intense power demands. For example, my portable gaming console runs longer and performs better with lithium batteries compared to other types. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) rechargeable batteries also serve as a strong alternative for AA or AAA devices, offering steady voltage and good cold-weather performance. However, I find that alkaline batteries struggle to keep up in high-drain scenarios. They lose power quickly, which leads to frequent replacements and reduced device performance.
Lithium batteries are the top choice for high-drain electronics due to their superior energy density, stable output, and reliability in demanding conditions.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries provide the best performance and longevity for high-drain devices, while NiMH rechargeables offer a solid backup option.
Best for Low-Drain Devices
For low-drain devices such as remote controls, wall clocks, and smoke alarms, I prefer using an alkaline battery. These devices draw small amounts of power over long periods, so I do not need the advanced features of lithium batteries. Alkaline batteries offer affordability, long shelf life, and steady energy delivery, making them ideal for household gadgets that do not require frequent battery changes.
Consumer electronics experts and manufacturers recommend alkaline batteries for low-drain applications because they are cost-effective and widely available. I use them in my remotes, clocks, and flashlights, and I rarely need to replace them. Their reliability and convenience make them a practical choice for backup batteries in emergency kits or for kids’ toys that may get lost or broken.
- Alkaline batteries are recommended for devices used occasionally.
- They are practical for budget-conscious users and backup needs.
- They provide stable power for simple electronics.
Alkaline batteries are the preferred solution for low-drain devices, offering dependable performance and excellent value.
Summary Point:
Alkaline batteries deliver reliable, long-lasting power for low-drain devices, making them the most practical and economical choice.
Environmental Impact

Recycling and Disposal
When I finish using batteries, I always think about how to dispose of them responsibly. Proper disposal matters because batteries contain materials that can harm the environment. I never throw lithium batteries in the regular trash. These batteries can cause fires and release toxic substances like lithium and cobalt. These chemicals can contaminate soil and water, which puts both people and wildlife at risk. Even though some places allow the disposal of an alkaline battery in household trash, I treat all batteries as electronic waste.
I bring my used batteries to designated drop-off locations or recycling centers. This practice helps prevent pollution and reduces the risk of fires in landfills. Recycling centers handle batteries safely, recovering valuable materials and keeping hazardous substances out of the environment.
- Improper disposal of lithium batteries can lead to fires.
- Toxic substances from batteries can pollute soil and water.
- Recycling batteries protects human health and wildlife.
I always recommend treating all batteries as electronic waste to minimize environmental risks.
Summary Point:
Proper recycling and disposal of batteries prevent pollution and protect the environment.
Eco-Friendliness
I care about the environmental impact of the products I use. When I choose batteries, I look for options that meet strict environmental standards. Many manufacturers now produce batteries free from mercury and cadmium. These improvements make batteries safer for the environment. I also check for certifications like EU/ROHS/REACH and SGS, which show that the batteries meet global safety and environmental requirements.
Recycling batteries not only reduces waste but also conserves resources. By returning used batteries to recycling programs, I help recover metals and reduce the need for new raw materials. This process lowers the overall environmental footprint of battery production and use.
Choosing batteries with eco-friendly certifications and recycling them supports a healthier planet.
Summary Point:
Eco-friendly batteries and responsible recycling reduce environmental harm and support sustainability.
Practical Recommendations
Everyday Household Devices
When I select batteries for everyday household devices, I focus on reliability and cost-effectiveness. Devices like wall clocks and smoke detectors require steady, long-lasting power but do not draw much current. I find that alkaline batteries perform very well in these applications. They offer a long shelf life, are affordable, and provide consistent performance for months or even over a year.
Here is a quick reference table for common household devices:
| Device Type | Performance | Recommended Replacement Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Clocks | Very Good | 12-18 months |
| Smoke Detectors | Good | Annual replacement |
I usually replace the batteries in my wall clocks every 12 to 18 months. For smoke detectors, I make it a habit to change them once a year. This schedule ensures my devices remain functional and safe. Alkaline batteries remain the most practical choice for these low-drain devices because they balance cost and reliability.
Summary Point:
Alkaline batteries are the best option for low-drain household devices due to their affordability, reliability, and long shelf life.
Electronics and Gadgets
When I power my electronics and gadgets, I look for batteries that deliver high energy density and long runtimes. Lithium batteries stand out in this category. They provide over twice the energy density of standard alkaline batteries, which means my devices run longer and perform better. I notice this difference most in smartphones, laptops, digital cameras, and portable gaming consoles. These devices often require sudden bursts of power or operate for extended periods, so I rely on lithium batteries for consistent voltage and dependable performance.
Lithium batteries also have a lower self-discharge rate. I can leave my devices unused for weeks, and they still retain most of their charge. This feature is especially useful for gadgets I do not use daily. The chart below highlights the performance differences between lithium and alkaline batteries across several criteria:
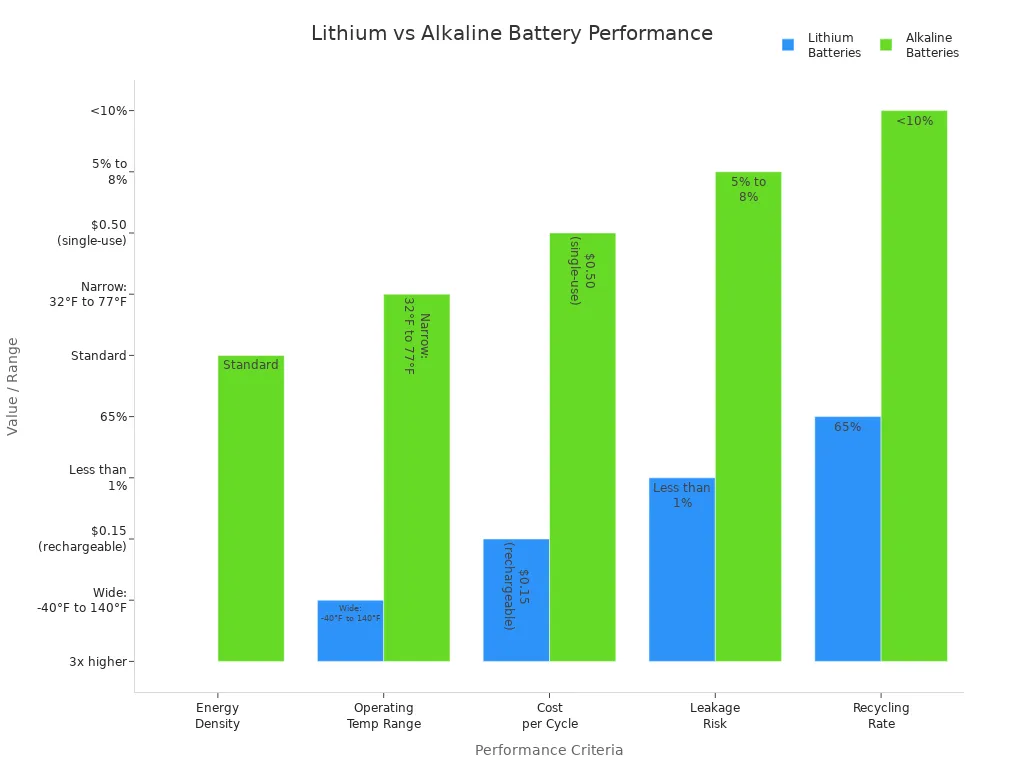
I also consider the environmental impact. Lithium batteries are more eco-friendly because I can recharge them many times and recycle them more easily. Over time, I save money and reduce waste, even though the initial cost is higher.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries provide superior performance, longer runtimes, and better environmental sustainability for high-demand electronics and gadgets.
Outdoor and Emergency Use
For outdoor and emergency use, I always choose batteries that can handle extreme conditions and deliver reliable power. Lithium batteries excel in this area. They operate consistently from -40°F to 140°F, which means my GPS units, emergency flashlights, and trail cameras work even in freezing winters or hot summers. I appreciate their lightweight design, especially when I pack gear for hiking or camping.
The table below compares lithium and alkaline batteries for outdoor and emergency devices:
| Feature/Aspect | Lithium Batteries | Alkaline Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -40°F to 140°F (consistent performance) | Significant loss below 50°F; may fail below 0°F |
| Shelf Life | ~10 years, minimal self-discharge, no leakage | ~10 years, gradual charge loss, risk of leakage |
| Runtime in High-Drain Devices | Up to 3x longer (e.g., 200 min vs 68 min in flashlight) | Shorter runtime, dims quickly |
| Weight | About 35% lighter | Heavier |
| Cold Weather Performance | Excellent, even better than alkaline at room temp | Major power loss or failure below freezing |
| Suitability for Outdoor Use | Ideal for GPS, emergency flashlights, trail cameras | Less reliable in cold or demanding conditions |
| Leakage Risk | Very low | Higher, especially after long storage |
I have tested lithium batteries in emergency flashlights and GPS trackers. They last much longer and stay bright, even after months in storage. I do not worry about leakage or sudden power loss, which gives me peace of mind during emergencies.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries are the top choice for outdoor and emergency devices because they deliver reliable, long-lasting power in extreme conditions and have a low risk of leakage.
Travel and Portable Use
When I travel, I always prioritize convenience, reliability, and weight. I want batteries that keep my devices running without frequent replacements or unexpected failures. Lithium batteries consistently meet these needs. They offer high energy density, which means I can carry fewer batteries and still power my devices for longer periods. This feature becomes essential when I pack for trips with limited space or strict weight restrictions.
I rely on lithium batteries for portable electronics such as wireless headphones, digital cameras, and GPS trackers. These devices often require steady voltage and long runtimes. Lithium batteries deliver consistent performance, even when I use them in different climates or altitudes. I have tested lithium batteries in both hot and cold environments. They maintain their charge and do not leak, which gives me peace of mind during long journeys.
Here is a comparison table that highlights the advantages of lithium batteries for travel and portable use:
| Feature | Lithium Batteries | Alkaline Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Energy Density | High | Moderate |
| Runtime | Extended | Shorter |
| Leakage Risk | Very low | Moderate |
| Temperature Tolerance | Wide range (-40°F to 140°F) | Limited |
| Shelf Life | Up to 10 years | Up to 10 years |
Tip: I always pack spare lithium batteries in my carry-on bag. Airlines allow them if I keep them in original packaging or protective cases.
I also consider the safety and regulations for battery transport. Most airlines restrict the number and type of batteries I can carry. Lithium batteries meet international safety standards and certifications, which makes them suitable for air travel. I check the airline’s guidelines before packing to avoid delays or confiscation.
When I travel internationally, I prefer rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. They reduce waste and save money over time. I use a portable charger to recharge my batteries on the go. This approach keeps my devices powered and eliminates the need to buy new batteries in unfamiliar locations.
Summary Points:
- Lithium batteries provide lightweight, long-lasting power for travel and portable devices.
- I choose lithium batteries for their reliability, safety, and compliance with airline regulations.
- Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries offer cost savings and environmental benefits during extended trips.
Alkaline Battery: When to Choose It
When I select batteries for my home or office, I often reach for an alkaline battery because it offers a practical balance of cost, availability, and performance. I find that the alkaline battery works best in devices that do not require a constant, high power draw. For example, I use them in remote controls, wall clocks, and toys. These devices operate efficiently with a standard alkaline battery, and I do not need to worry about frequent replacements.
I choose alkaline batteries for several reasons:
- They have a lower upfront cost, which helps me manage my budget when I need to power multiple devices.
- I can find them easily in most stores, so I never have trouble replacing them.
- Their long shelf life, often up to 10 years, means I can store extras for emergencies without worrying about them losing charge.
- They are safe and reliable for everyday use, especially in devices that I use occasionally or for short periods.
Consumer reports recommend alkaline batteries for common household items such as toys, game controllers, and flashlights. I notice that they perform well in these devices, providing steady power without unnecessary expense. For devices that I use infrequently or that are easy to access, I always choose an alkaline battery. In contrast, I reserve lithium batteries for high-drain electronics or situations where long-term stability is critical.
| Device Type | Recommended Battery Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Controls | Alkaline battery | Low power, cost-effective |
| Wall Clocks | Alkaline battery | Long shelf life, reliable |
| Toys | Alkaline battery | Affordable, easy to replace |
Summary Point:
I choose an alkaline battery for low-drain, everyday devices because it is affordable, widely available, and dependable.
When I choose between lithium and alkaline batteries, I focus on my device’s needs, usage habits, and environmental priorities. Lithium batteries excel in high-drain, outdoor, and long-term applications due to their higher energy density, longer shelf life, and reliable performance in extreme temperatures. For everyday, low-drain devices or when I want to save money, I select an alkaline battery. The table below summarizes key factors to help me decide:
| Factor | Lithium Batteries | Alkaline Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Standard |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Shelf Life | Up to 20 years | Up to 10 years |
| Best Use | High-drain, outdoor | Low-drain, everyday |
I always match the battery type to my device for the best performance and value.
FAQ
What devices work best with lithium batteries?
I use lithium batteries in high-drain devices like cameras, GPS units, and portable gaming consoles. These batteries deliver steady power and last longer in demanding electronics.
Summary Point:
Lithium batteries excel in devices that require consistent, high energy output.
Can I mix lithium and alkaline batteries in the same device?
I never mix lithium and alkaline batteries in one device. Mixing types can cause leakage, reduced performance, or even damage to my electronics.
Summary Point:
Always use the same battery type in a device for safety and optimal performance.
How do I store batteries for emergencies?
I store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. I keep lithium batteries partially charged and avoid freezing them. I check expiration dates regularly.
| Storage Tip | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cool, dry location | Prevents degradation |
| Avoid sunlight | Maintains shelf life |
Summary Point:
Proper storage extends battery life and ensures reliability during emergencies.
Are lithium batteries more environmentally friendly than alkaline batteries?
I choose lithium batteries for their rechargeability and lower waste. Many lithium batteries meet strict environmental standards and certifications.
Summary Point:
Rechargeable lithium batteries reduce waste and support sustainability.
Post time: Aug-18-2025





